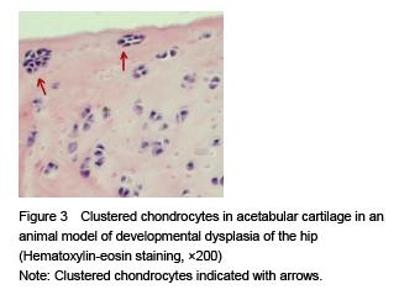
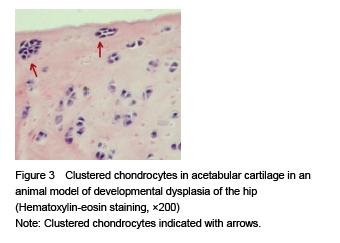
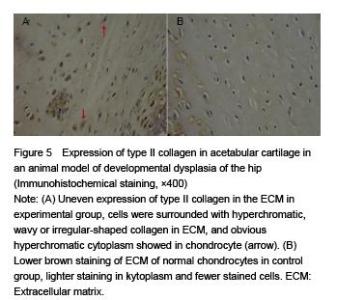
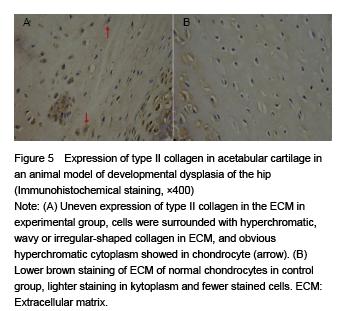
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 7879-7884.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
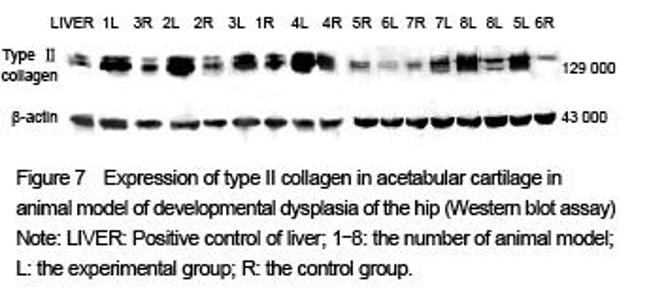
Type II collagen expression in a rabbit model of developmental dysplasia of the hip
- Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Medical University Affiliated Suzhou Hospital (Suzhou Municipal Hospital), Suzhou 215002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-28Online:2015-11-30Published:2015-11-30 -
Contact:Chen Guang-xiang, Master, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Medical University Affiliated Suzhou Hospital (Suzhou Municipal Hospital), Suzhou 215002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Xiang-xin, Ph.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Medical University Affiliated Suzhou Hospital (Suzhou Municipal Hospital), Suzhou 215002, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Xiang-xin, Chen Guang-xiang, Cheng Liang, Xu Ren-jie, Zou Tian-ming. Type II collagen expression in a rabbit model of developmental dysplasia of the hip[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(49): 7879-7884.
share this article
| [1] Peled E, Eidelman M, Katzman A, et al. Neonatal incidence of hip dysplasia: ten years of experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(4):771-775.
[2] Mahan ST, Kasser JR. Does swaddling influence developmental dysplasia of the hip? Pediatrics. 2008; 121(1): 177-178..
[3] Kokavec M, Bialik V. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Prevention and real incidence. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2007; 108(6):251-254.
[4] Yiv BC, Saidin R, Cundy PJ, et al. Developmental dysplasia of the hip in South Australia in 1991: prevalence and risk factors. J Paediatr Child Health. 1997;33(2):151-156.
[5] Chan A, McCaul KA, Cundy PJ, et al. Perinatal risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997;76(2):F94-100.
[6] Patel H; Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care. Preventive health care, 2001 update: screening and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. CMAJ. 2001;164(12):1669-1677.
[7] Synder M, Harcke HT, Domzalski M. Role of ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of developmental dysplasia of the hip: an international perspective. Orthop Clin North Am. 2006;37(2):141-147, v.
[8] Shimogaki K, Yasunaga Y, Ochi M. A histological study of articular cartilage after rotational acetabular osteotomy for hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7):1019-1023.
[9] Greenhill BJ, Hainau B, Ellis RD, et al. Acetabular changes in an experimental model of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15(6):789-793.
[10] Bo N, Peng W, Xinghong P, et al. Early cartilage degeneration in a rat experimental model of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(6): 513-520.
[11] Martel-Pelletier J, Boileau C, Pelletier JP, et al. Cartilage in normal and osteoarthritis conditions. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22(2):351-384.
[12] Brandt KD, Dieppe P, Radin E. Etiopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Med Clin North Am. 2009;93(1):1-24, xv.
[13] Dudkiewicz I, Salai M, Ganel A, et al. Total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 30 years of age following developmental dysplasia of hip (DDH) in infancy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2002;122(3):139-142.
[14] Thomas SR, Wedge JH, Salter RB. Outcome at forty-five years after open reduction and innominate osteotomy for late-presenting developmental dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(11):2341-2350.
[15] Aigner T, Hemmel M, Neureiter D, et al. Apoptotic cell death is not a widespread phenomenon in normal aging and osteoarthritis human articular knee cartilage: a study of proliferation, programmed cell death (apoptosis), and viability of chondrocytes in normal and osteoarthritic human knee cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(6):1304-1312.
[16] Rubini M, Cavallaro A, Calzolari E, et al. Exclusion of COL2A1 and VDR as developmental dysplasia of the hip genes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(4):878-883.
[17] Wilkinson JA. Prime factors in the etiology of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1963;45-B(2): 268-283.
[18] Michaeli DA, Murphy SB, Hipp JA. Comparison of predicted and measured contact pressures in normal and dysplastic hips. Med Eng Phys. 1997;19(2):180-186.
[19] Sandell LJ, Aigner T. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis. An introduction: cell biology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. 2001;3(2):107-113.
[20] Ala-Kokko L, Baldwin CT, Moskowitz RW, et al. Single base mutation in the type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) as a cause of primary osteoarthritis associated with a mild chondrodysplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(17): 6565-6568.
[21] Knowlton RG, Katzenstein PL, Moskowitz RW, et al. Genetic linkage of a polymorphism in the type II procollagen gene (COL2A1) to primary osteoarthritis associated with mild chondrodysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322(8):526-530.
[22] Sandell LJ. Etiology of osteoarthritis: genetics and synovial joint development. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(2):77-89.
[23] Aigner T, Stöss H, Weseloh G, et al. Activation of collagen type II expression in osteoarthritic and rheumatoid cartilage. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;62(6): 337-345.
[24] Stoop R, Buma P, van der Kraan PM, et al. Type II collagen degradation in articular cartilage fibrillation after anterior cruciate ligament transection in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(4):308-315.
|
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||